
Overpopulation is a pressing global problem with far-reaching economic implications. As the world’s population continues to grow at an unprecedented rate, exceeding 7.9 billion people, the strain on resources, infrastructure and the economy is becoming increasingly clear. In this text, we examine thirteen surprising economic effects of overpopulation and their impact on societies all over the world.
1. Pressure on infrastructure

One of essentially the most immediate economic impacts of overpopulation is the strain on infrastructure. With population growth, the necessity for housing, transportation, water and energy increases exponentially, leading to congested roads, overwhelmed utilities and a deterioration in public services. Governments must invest significant resources in expanding and maintaining infrastructure to accommodate growing populations. This places a major financial burden on taxpayers and hinders economic development.
2. Scarce resources

Overpopulation exacerbates resource scarcity as finite resources corresponding to water, food and energy grow to be increasingly scarce to satisfy the needs of a growing population. Competition for resources is intensifying, resulting in higher prices, supply shortages and environmental degradation. These shortages can hinder economic growth, exacerbate inequality and contribute to social unrest and conflict in resource-poor regions.
3. Reduced quality of life

Overpopulation can result in a deterioration in the standard of lifetime of residents, as overcrowding, pollution and concrete sprawl reduce the standard of life in densely populated areas. Housing shortages, inadequate infrastructure and environmental degradation can affect residents’ well-being and affect their access to essential services and amenities. This reduced quality of life can negatively impact mental and physical health, productivity and overall societal well-being.
4. Overburdened healthcare systems
Growing populations are placing enormous pressure on healthcare systems as demand for medical services and resources outstrips capability. Overcrowded hospitals, long wait times, and limited access to healthcare providers can reduce the standard and effectiveness of healthcare, resulting in poorer health outcomes and better healthcare costs. Governments must put money into expanding health infrastructure and services to satisfy the needs of growing populations, further straining already strained budgets.
5. Unemployment and underemployment

Overpopulation can exacerbate unemployment and underemployment because the availability of labor exceeds demand in lots of sectors of the economy. High population growth rates can outpace job creation efforts, resulting in a labor surplus and increased competition for limited job opportunities. This oversupply of staff can depress wages, exacerbate income inequality, and hinder economic mobility, especially for vulnerable populations.
6. Environmental destruction

Overpopulation accelerates environmental degradation as increased human activity and consumption puts unsustainable pressure on natural ecosystems and resources. Deforestation, habitat destruction, pollution and climate change are among the many environmental problems exacerbated by overpopulation, causing irreversible damage to biodiversity and ecosystems. The economic costs of environmental degradation, including lack of ecosystem services, reduced agricultural productivity and increased health care spending, are significant and might hinder long-term economic growth and sustainability.
7. Food insecurity

Overpopulation contributes to food insecurity because demand for food exceeds agricultural production and distribution capability. Growing populations are straining agricultural resources, water supplies and arable land, making it increasingly difficult to adequately feed the growing population. Food shortages, rising prices and malnutrition are amongst the implications of food insecurity brought on by overpopulation, particularly in regions with limited access to resources and vulnerable populations.
8. Increased poverty

Overpopulation can exacerbate poverty and income inequality as limited resources grow to be scarce amongst growing populations, resulting in increased competition for scarce opportunities and resources. In densely populated areas, access to education, healthcare and employment might be limited, making a vicious cycle of poverty and socioeconomic drawback. Addressing the basis causes of overpopulation and implementing policies to advertise sustainable development and equitable distribution of resources are critical to reducing poverty and promoting inclusive economic growth.
9. Pressure on education systems

Rapid population growth is putting strain on education systems as governments struggle to accommodate growing numbers of scholars and supply quality education to all. Overcrowded classrooms, inadequate facilities and limited resources can undermine the standard of education and harm students’ academic performance and future prospects. Investments in educational infrastructure, teacher training and access to educational resources are critical to handle the challenges of overpopulation and ensure equal access to education for all.
10. Challenges of urbanization
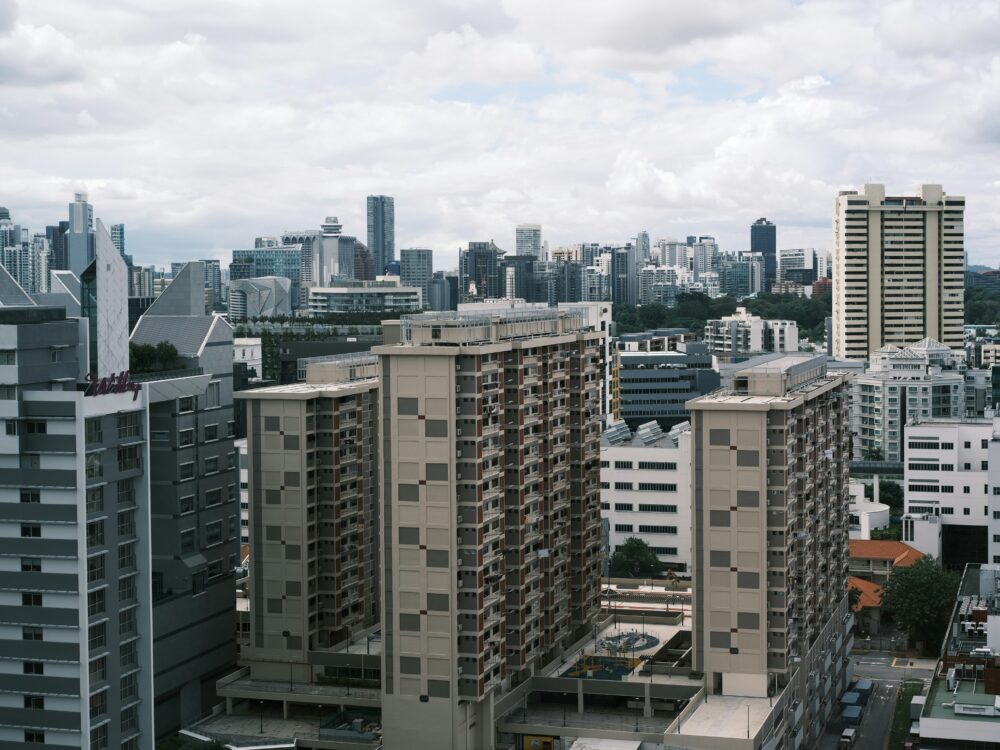

Overpopulation is driving rapid urbanization as people flock to cities in the hunt for work, education and opportunity. While urbanization can spur economic growth and development, it also poses significant challenges, including housing shortages, traffic congestion and environmental degradation. Addressing the impacts of urbanization requires careful planning, investment in infrastructure and measures to advertise sustainable and inclusive growth.
11. Pressure on social services

Growing populations are straining social services corresponding to welfare, child care, and social assistance programs as governments with limited resources struggle to satisfy the needs of growing populations. Overcrowded housing, long waiting lists for public housing, and inadequate support services can exacerbate poverty and social inequality, particularly for vulnerable populations. Investing in social services and implementing policies to handle the basis causes of overpopulation are critical to promoting social cohesion and equal access to support services.
12. Migration pressure

Overpopulation can increase migration pressures as people seek to flee crowded and resource-poor regions to seek out higher opportunities and a greater quality of life elsewhere. Migration can place strain on host communities and exacerbate social tensions, particularly in regions already scuffling with limited resources and economic challenges. Addressing the causes of overpopulation and promoting sustainable development and resource management are crucial to alleviating migratory pressures and promoting stability and prosperity.
13. Tax challenges

Overpopulation poses significant financial challenges for governments as they have to allocate resources to satisfy the needs of the growing population while balancing competing priorities and budget constraints. Investments in infrastructure, healthcare, education and social services to accommodate growing populations require significant financial resources, strain government budgets and hinder long-term economic stability and sustainability. Implementing policies to handle the basis causes of overpopulation and promote sustainable development and resource management is critical to addressing these fiscal challenges and promoting economic resilience and prosperity.
Overpopulation

In summary, overpopulation poses significant economic challenges with far-reaching impacts on societies all over the world. Addressing these challenges requires coordinated efforts to advertise sustainable development, equitable resource management and population stabilization. By understanding the economic impacts of overpopulation and implementing targeted policies and interventions, governments and communities can mitigate the results of overpopulation and create a more sustainable and prosperous future for all.

